Markaccy’s Decentralised Digital Health Systems Reformation
The core aim of digital transformation is to utilize technology in creating faster and smarter solutions to practical problems. Healthcare is a crucial sector where the faster and smarter solutions provided by digital technologies have a strong impact. In economies where poor healthcare systems translate to low life expectancies and death from curable diseases, digital technologies can help reduce death rates through a focus on preventive healthcare. This has already begun to show positive results, as in previous years, Africa had experienced high mortality rates numbering to over 38 million deaths from Non-Communicable Diseases, and the use of mobile technologies in proliferating preventive healthcare has reduced this number. Another practical illustration is the ReMIND Programme which used mHealth applications to reduce maternal deaths (16.4%) and infant deaths (5.2%) over a 10 year period in the Uttar Pradesh region in India.
Digital health systems are built with digital health platforms, digital diagnostics and digital health innovations as tools for delivering healthcare. Digital health platforms explore means of this healthcare delivery, such as mobile applications and blockchain-enabled decentralised apps. Digital diagnostics cover medical diagnosis from data analytics and medical research. Digital innovations explore inventions that support preventive, curative, and diagnostic healthcare, like blockchain electronic health records. These are the core components of connected health or technology-enabled health.
There is, however, so much that blockchain can achieve with digital health systems. Blockchain brings with it the advantage of transparency and decentralisation in peer-to-peer interconnectivity, eliminating the control that centralised hospitals have in managing patient data and relinquishing control of this data to patients on the blockchain, thus enforcing the importance of data privacy which is a critical aspect of trust. Also, blockchain provides access to Non-Emergency Medical Transportation, which is a response to people missing appointments due to a lack of reliable transportation to medical facilities, especially for patients who live in remote areas. This helps to save money from missed appointments, which is an addition to the already familiar advantage of cost-cutting solutions that blockchain offers.
Markaccy, a Blockchain Technology Company that operates a service-based marketplace model, is looking to expand operations in decentralised digital health using blockchain. Markaccy sees its decentralised Digital Health Systems Project as a crucial component to its Digital Economy, but the Digital Health Systems create a unique opportunity to generate immense value by demonstrating the power of blockchain to end-users.
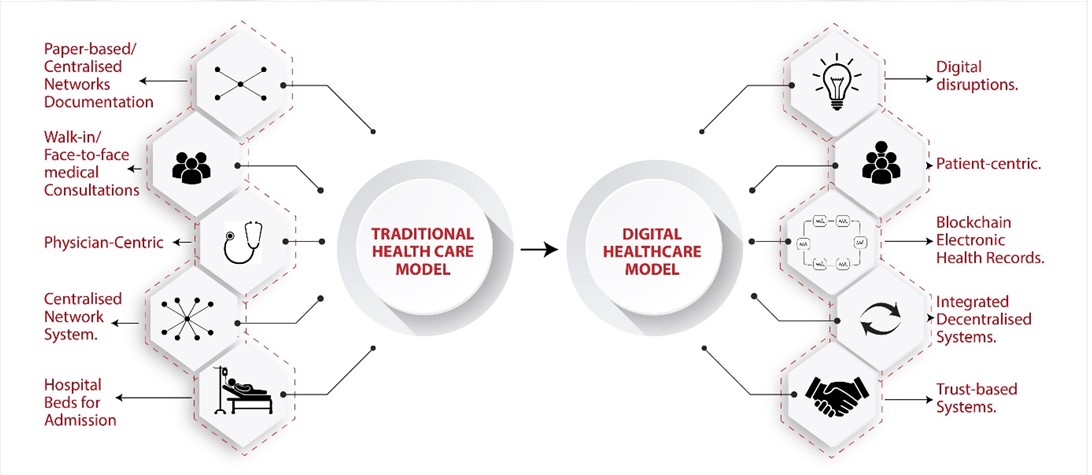
Transforming Traditional Medical Centres into Decentralised Digital Health Fortresses
There are two common health models in the health industry. There is a traditional health model run by conventional hospitals. These hospitals are walk-in centers for face-to-face consultations and treatments. Some might have digital systems to support their conventional models, whilst other unequipped hospitals function purely as traditional models.
Then, there are digital models set-up purely to disrupt conventional models. These are hospitals without beds that are purely digital, with doctors, nurses, and other health practitioners connected to laptops and iPads and connecting with patients. An example of this model is the Mercy Virtual Hospital which goes as far as donating iPads to patients. Doctors can check vital signs of patients through iPads and also give diagnosis on health conditions. Markaccy’s Decentralised Digital Health Systems Reformation
The core aim of digital transformation is to utilise technology in creating faster and smarter solutions to practical problems. Healthcare is a crucial sector where the faster and smarter solutions provided by digital technologies have a strong impact. In economies where poor healthcare systems translate to low life expectancies and death from curable diseases, digital technologies can help reduce death rates through a focus on preventive healthcare. This has already begun to show positive results , as in previous years, Africa had experienced high mortality rates numbering to over 38 million deaths from Non-Communicable Diseases, and the use of mobile technologies in proliferating preventive healthcare has reduced this number. Another practical illustration is the ReMIND Programme which used mHealth applications to reduce maternal deaths (16.4%) and infant deaths (5.2%) over a 10 year period in the Uttar Pradesh region in India.
Digital health systems are built with digital health platforms, digital diagnostics, and digital health innovations as tools for delivering healthcare. Digital health platforms explore means of this healthcare delivery, such as mobile applications and blockchain-enabled decentralised apps. Digital diagnostics cover medical diagnosis from data analytics and medical research. Digital innovations explore inventions that support preventive, curative, and diagnostic healthcare, like blockchain electronic health records. These are the core components of connected health or technology enabled health.
There is, however, so much that blockchain can achieve with digital health systems. Blockchain brings with it the advantage of transparency and decentralisation in peer-to-peer interconnectivity, eliminating the control that centralised hospitals have in managing patient data and relinquishing control of this data to patients on the blockchain, thus enforcing the importance of data privacy which is a critical aspect of trust. Also, blockchain provides access to Non-Emergency Medical Transportation, which is a response to people missing appointments due to a lack of reliable transportation to medical facilities, especially for patients who live in remote areas. This helps to save money from missed appointments, which is an addition to the already familiar advantage of cost-cutting solutions that blockchain offers.
Markaccy, a Blockchain Technology Company that operates a service-based marketplace model, is looking to expand operations in decentralised digital health using blockchain. Markaccy sees its decentralised Digital Health Systems Project as a crucial component to its Digital Economy, but the Digital Health Systems create a unique opportunity to generate immense value by demonstrating the power of blockchain to end-users.
Transforming Traditional Medical Centres into Decentralised Digital Health Fortresses
There are two common health models in the health industry. There is a traditional health model run by conventional hospitals. These hospitals are walk-in centres for face-to-face consultations and treatments. Some might have digital systems to support their conventional models, whilst other unequipped hospitals function purely as traditional models.
Then, there are digital models set-up purely to disrupt conventional models. These are hospitals without beds that are purely digital, with doctors, nurses and other health practitioners connected to laptops and iPads and connecting with patients. An example of this model is the Mercy Virtual Hospital which goes as far as donating iPads to patients. Doctors can check vital signs of patients through iPads and also give diagnosis on health conditions.
Markaccy’s Digital Hospital Transformation Model
Markaccy focuses on something different. First, it aims to set up a hospital running a traditional model, with beds, walk-in appointments and consultations and face-to-face treatments. Then ultimately, over time, it will convert this traditional model Hospital into a purely digital Hospital without beds. The aim of this procedural transformation is to embark on an experiential journey of learning, and to leverage on invaluable firsthand knowledge of the process of converting traditional models into digital models, which will be crucial for Markaccy’s Digital Economy. Despite the resource intensiveness it will command, a conversion from a traditional model healthcare system into a decentralised Digital Health System powered by blockchain will yield both long term benefits and economies of scale.
To achieve this transformation, Markaccy will embark on the following steps:
1) Improve Research, Data Collection and Databases: The very first step, after set-up of hospitals in target geographical locations of Africa, South-East Asia and Central America, is the improvement of research and information management, and building databases to support data storage and distribution. Data distribution will include sending preventive health tips to patients phones, and this is feasible because 2G networks covered 90% of the population of sub-Saharan Africa, and 60% of the sub-Saharan African population should be covered by 3G networks in 2025. This is the very first step to going digital, which will incorporate data analytics and management. A huge part of this research will also include collaboration with respective agencies on the need for migration into digital systems in a reliable public-private partnership which will not only quicken this transition, but will also ensure for ease of data collection and distribution, and also improved research.
2) Enable Blockchain Electronic Health Records: This is another crucial step which involves the gradual integration of clinical data into the blockchain, so it can be accessed from decentralised peer-to-peer points. To attain this point of management of Electronic Health Records, Markaccy will need to have attained streamlined and efficient management, and achieving the first step above will create the time for the efficient management alignment required.
3) Developing Required Supply, Value and Distribution Chains: Effective supply and value chains need to compliment a digital system. At this stage, Markaccy will begin to implement strategies to connect patients in remote and inaccessible areas. There will be a need to also create strategically distributed access centres for curative care and treatment, as well as proliferate retail clinic models in chosen partner supermarkets to improve accessibility to healthcare. The retail clinic model will work efficiently after Electronic Health Records(EHR) has been set-up and embedded into Markaccy’s Blockchain.
4) Creating Lean Hospitals: The next step will be to create lean hospitals by replacing face-to-face consultations with consultations over mHealth and digital technology platforms. This will also be followed by reducing admissions to emergency cases. This is to save the patient time, improve doctor-patient relationship and reduce incidence of missed appointments which is cost-intensive.
5) Integrating Digital Health Systems into Decentralised Apps: This represents the final step in the overhaul of the traditional healthcare set-up into a decentralised Digital Health System. Patients, doctors, investors and training institutes will be integrated into a decentralised app where interaction is real time and peer-to-peer. Over time, the aim is to expand the integration of other hospitals into Markaccy’s blockchain, enabling a wider reach and thus creating more value. Markaccy Hospitals will have no beds at this point, and the focus will be on managing digital interfaces and resources, which will all be connected to the blockchain.
The need to undergo this transformation from traditional health systems to decentralised digital health systems will become a strong source of experiential learning for Markaccy and will establish decentralised digitalisation as a strong competence which is invaluable as a resource for future projects. And like other digital components which Markaccy aims to strengthen, this is how Markaccy’s Digital Health Systems will be strengthened in the journey of creating a Digital Economy.